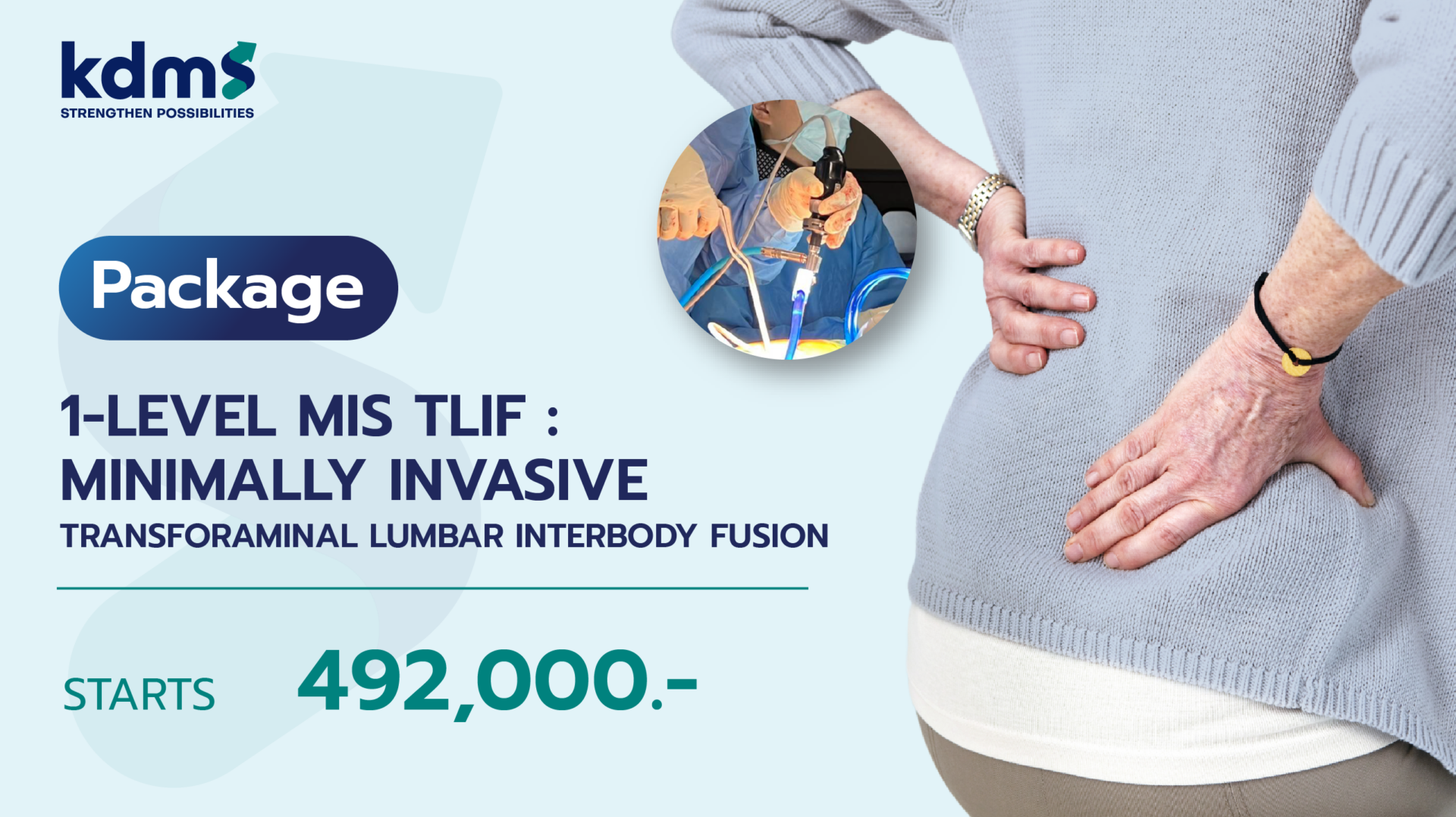
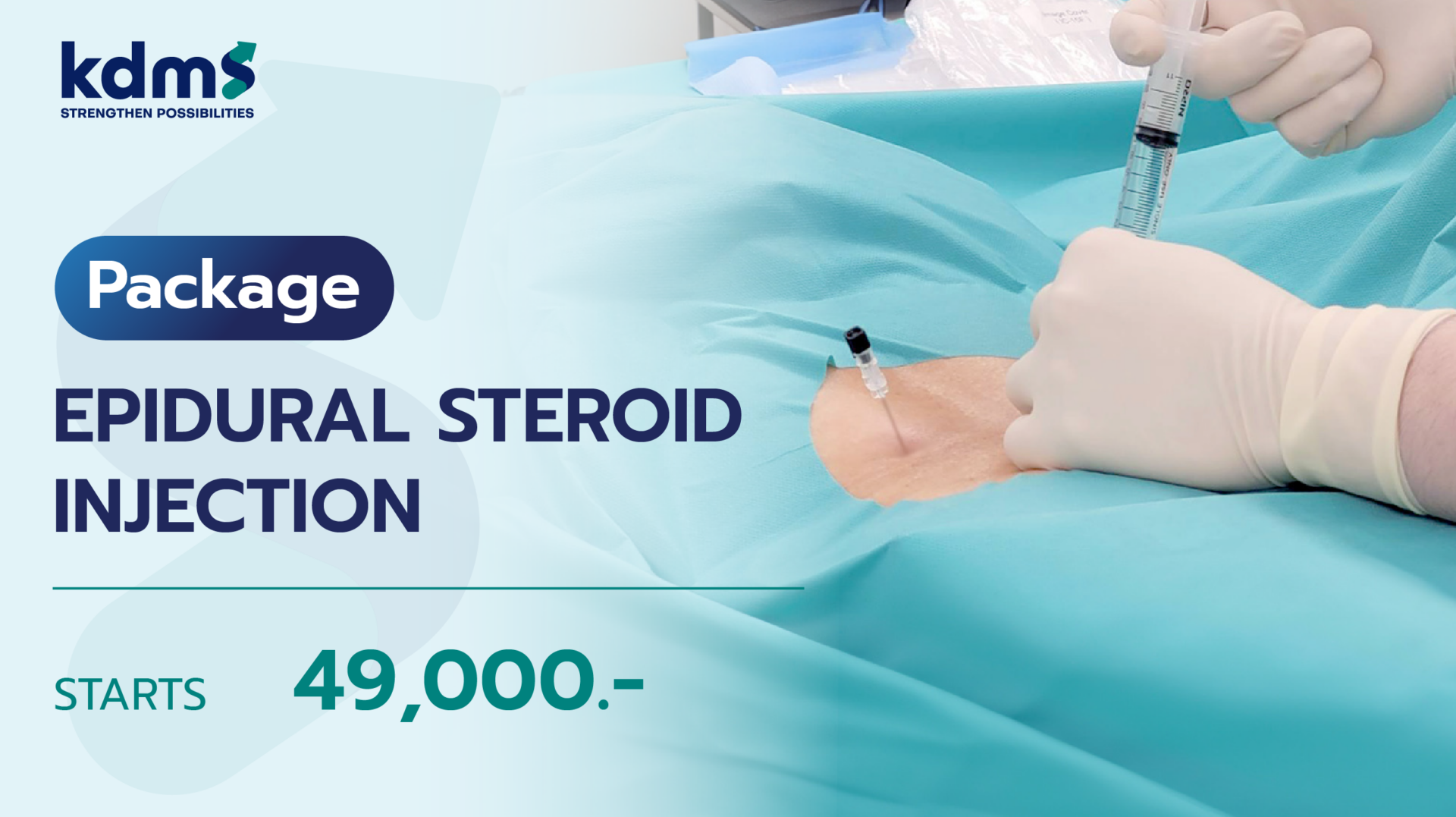
ไขข้อสงสัย ปวดหลังเกิดจากอะไร พร้อมสัญญาณเตือนที่ควรต้องรู้
ในชีวิตคนเราต้องเคยปวดหลังสักครั้งหนึ่งเป็นเรื่องปกติ ยิ่งหากลองสังเกตในคนรอบๆ ตัว เชื่อได้ว่าต้องเคยได้ยินคนบ่นว่าปวดหลังแน่นอน โดยเฉพาะในกลุ่มผู้สูงอายุ
ปวดหลัง นับว่าเป็นอาการที่พบได้บ่อยคนในยุคนี้ กล่าวคือไม่ใช่เฉพาะผู้สูงอายุเท่านั้นที่จะประสบปัญหานี้ แต่ในคนวัยหนุ่มสาวก็สามารถพบได้มากเช่นกัน เนื่องมาจากไลฟ์สไตล์การทำงานและชีวิตประจำวันที่ต้องนั่งอยู่หน้าจอเกือบตลอดเวลา หรืออาจมาจากความเสื่อมเพราะการใช้งานหนักมาเป็นระยะเวลานานก็เป็นอีกสาเหตุหนึ่งเช่นกัน
Table of Contents
รู้หรือไม่..อาการปวดหลังเกิดได้จากหลายสาเหตุ
เมื่อผู้ป่วยมีอาการปวดหลัง แพทย์จะเริ่มต้นด้วยการซักประวัติเพื่อนำไปสู่การวินิจฉัยแยกโรคที่เป็นสาเหตุของอาการได้ โดยสามารถแบ่งออกเป็นกลุ่มต่างๆ ดังนี้
- ความเสื่อม (Degenerative) ส่วนใหญ่พบในผู้สูงอายุ ซึ่งเป็นเพราะหมอนรองกระดูกสันหลังที่เสื่อมไปตามวัยจนเกิดการทรุด และเป็นสาเหตุที่ทำให้ปวดหลังหรือกดทับเส้นประสาทได้
- ใช้งานมากเกินไป (Overuse) พบได้บ่อยในกลุ่มของผู้ที่มีอาการออฟฟิศซินโดรมที่มักจะใช้งานในท่าทางที่ซ้ำๆ นานๆ และไม่ถูกสุขลักษณะ รวมทั้งกลุ่มของผู้ที่ใช้งานหนักในบางกิจกรรม เช่น ต้องยกของหนักเป็นประจำ
- อุบัติเหตุ (Trauma) อาจมีอาการปวดหลังเนื่องมาจากอุบัติเหตุรุนแรง เช่น อุบัติเหตุจราจร หรือตกจากที่สูง ซึ่งปัญหาที่พบคือกระดูกหัก กระดูกเคลื่อน หรือเส้นประสาทได้รับบาดเจ็บ แต่หากเป็นอุบัติเหตุที่ไม่รุนแรง เช่น ล้มกระแทก หรือบาดเจ็บจากการเล่นกีฬา ซึ่งเป็นการบาดเจ็บเฉพาะจุด กรณีนี้อาการปวดจะขึ้นอยู่กับความรุนแรงของอุบัติเหตุนั้นๆ
- เนื้องอกที่กระดูกสันหลัง (Tumor) เป็นกลุ่มอาการในผู้ป่วยโรคมะเร็งที่เนื้องอกกระจายมาที่กระดูกสันหลัง โดยจะรู้สึกปวดหลังเมื่อโครงสร้างกระดูกเริ่มสูญเสียความแข็งแรงจากการลุกลามของโรค ส่วนใหญ่จะพบในผู้สูงอายุ
- ภาวะติดเชื้อ (Infection) เป็นอาการปวดของกระดูกสันหลังเนื่องจากการติดเชื้อ โดยผู้ป่วยมักจะมีอาการปวดหลังพร้อมกับมีไข้ร่วมด้วย
เช็กอาการปวดหลังเบื้องต้น ปวดแบบไหนคือสัญญาณอันตราย
บางครั้งอาการปวดหลังก็ไม่ใช่เรื่องปกติเสมอไป ซึ่งผู้ป่วยควรหมั่นสังเกตตัวเองว่ามีอาการอื่นๆ ร่วมด้วยหรือไม่ เพราะนี่อาจเป็นสัญญาณเตือนที่บ่งชี้ถึงความผิดปกติบางอย่าง (Red Flag Sign) ซึ่งควรให้แพทย์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญตรวจอย่างละเอียด ได้แก่
- ปวดหลังร่วมกับมีไข้ อาจสัมพันธ์กับภาวะติดเชื้อ
- รู้สึกเบื่ออาหาร หรือน้ำหนักลดอย่างรวดเร็ว อาจเป็นสัญญาณของโรคมะเร็ง
- มีอาการชาหรืออ่อนแรงร่วมด้วย อาจเกี่ยวข้องกับการกดทับของเส้นประสาท
- การขับถ่ายที่ผิดปกติ เช่น ปัสสาวะไม่ออก กลั้นอุจจาระไม่ได้ สันนิษฐานได้ว่าเกิดจากการกดทับเส้นประสาทที่ทำให้การขับถ่ายผิดปกติ
- ปวดหลังเรื้อรังมากกว่า 3 เดือนขึ้นไป ถือว่าเป็นระยะเวลาของการปวดที่นานกว่าปกติ และควรรับการวินิจฉัยจากแพทย์เพื่อหาสาเหตุที่แน่ชัด
- ปวดหลังจากอุบัติเหตุ อาจพบว่ามีกระดูกสันหลังหักยุบได้
แนวทางการรักษาอาการปวดหลังมีอะไรบ้าง
หลังจากผู้ป่วยได้รับการวินิจฉัยเบื้องต้นจากการซักประวัติ ตรวจร่างกาย เอกซเรย์ หรือ MRI เมื่อรู้ถึงปัญหาที่แท้จริงแล้ว แนวทางการรักษาของแพทย์ในขั้นตอนต่อมาจะเป็นไปใน 3 รูปแบบ ดังนี้
- รักษาด้วยการใช้ยา (Medication) จะเป็นการจ่ายยาตามโรคของผู้ป่วย เช่น ยาแก้ปวด, ยาลดการอักเสบ, ยาคลายกล้ามเนื้อ หรือยาลดความปวดของระบบประสาท เป็นต้น
- รักษาโดยไม่ใช้ยา (Non-medication)
- กายภาพบำบัด เช่น การนวด อัลตราซาวด์ การใช้เลเซอร์ รวมไปถึงการทำช็อกเวฟเพื่อคลายกล้ามเนื้อ ลดอาการปวด นอกจากนี้ยังมีท่ากายบริหารยืดเหยียดและเสริมสร้างความแข็งแรงให้กล้ามเนื้อ
- การปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมของผู้ป่วย แพทย์จะวิเคราะห์จากการซักประวัติว่าผู้ป่วยมีพฤติกรรมที่ไม่ถูกต้องอย่างไรบ้าง และควรแก้ไขอย่างไร
- รักษาด้วยการผ่าตัด (Operative treatment) จะเกิดขึ้นในกรณีของผู้ป่วยที่ผ่านการรักษาใน 2 รูปแบบข้างต้นมาแล้ว แต่ยังไม่หาย และเป็นโรคปวดหลังที่สามารถแก้ไขด้วยวิธีการผ่าตัดได้ เช่น โรคหมอนรองกระดูกกดทับเส้นประสาท หรือกระดูกสันหลังเสื่อมกดทับเส้นประสาท เป็นต้น
หากไม่อยากปวดหลัง ต้องเริ่มปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมตั้งแต่เนิ่นๆ
- ใช้งานหลังอย่างเหมาะสม ไม่ยกของหนักโดยไม่จำเป็น ปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมที่ผิดสุขลักษณะ เช่น การนั่งนานเกินไป หรือนั่งในท่าทางที่เป็นอันตรายต่อกระดูกสันหลัง
- หมั่นเสริมสร้างความแข็งแรงของกล้ามเนื้อหลัง ด้วยการบริหารร่างกาย ยืดเหยียดกล้ามเนื้ออย่างสม่ำเสมอ โดยเฉพาะกล้ามเนื้อท้องและกล้ามเนื้อหลังที่เป็น Core Muscle เพื่อเพิ่มความแข็งแรงยืดหยุ่น
- ควบคุมน้ำหนักตัวให้อยู่ในระดับปกติ หากมีน้ำหนักตัวที่มากเกินไป จะทำให้กระดูกสันหลังทำงานหนักขึ้น อาจทำให้ปวดหลังได้ง่าย เพราะต้องรับน้ำหนักมากตามไปด้วย
อาจกล่าวได้อาการปวดหลังนั้น ที่พบบ่อยสุดคือเกิดจากความเสื่อมไปตามวัย รองลงมาคือเกิดจากพฤติกรรมการใช้งานที่ไม่เหมาะสม เมื่อไม่อยากประสบปัญหาปวดหลังก่อนวัยอันควร ต้องเริ่มต้นดูแลตัวเองตั้งแต่วันนี้ ก่อนที่โครงสร้างหลักของร่างกายอย่างกระดูกสันหลังของเราจะค่อยๆ เสื่อมลงโดยไม่สามารถเรียกคืนกลับมาได้อีกต่อไป…
Q&A
Q: ทำไมเราถึงปวดหลังเวลาที่นั่งทำงานนานๆ
จริงๆ แล้วในทุกๆ การเคลื่อนไหว ไม่ว่าจะนั่ง เดิน ยืน หรือนอน กระดูกสันหลังที่เป็นแกนกลางของร่างกายกำลังทำหน้าที่รับน้ำหนักของเราอยู่ตลอดเวลา นั่นหมายความว่าถ้าเราทำกิจวัตรประจำวันในท่าทางที่ไม่ถูกต้อง กระดูกสันหลังก็จะทำงานมากขึ้น จนอาจก่อให้เกิดอาการปวดหลังตามมา
เคยมีผลการศึกษาออกมาแล้วว่าท่าทางต่างๆ ในชีวิตประจำวันของเราส่งผลต่อการรับน้ำหนักของกระดูกสันหลังแตกต่างกันอย่างไรบ้าง ซึ่งหลายคนอาจไม่เคยคาดคิดมาก่อนว่าการนั่งทำงานหน้าคอมพิวเตอร์เป็นเวลานานจะส่งผลต่อหลังมากกว่าที่คิด
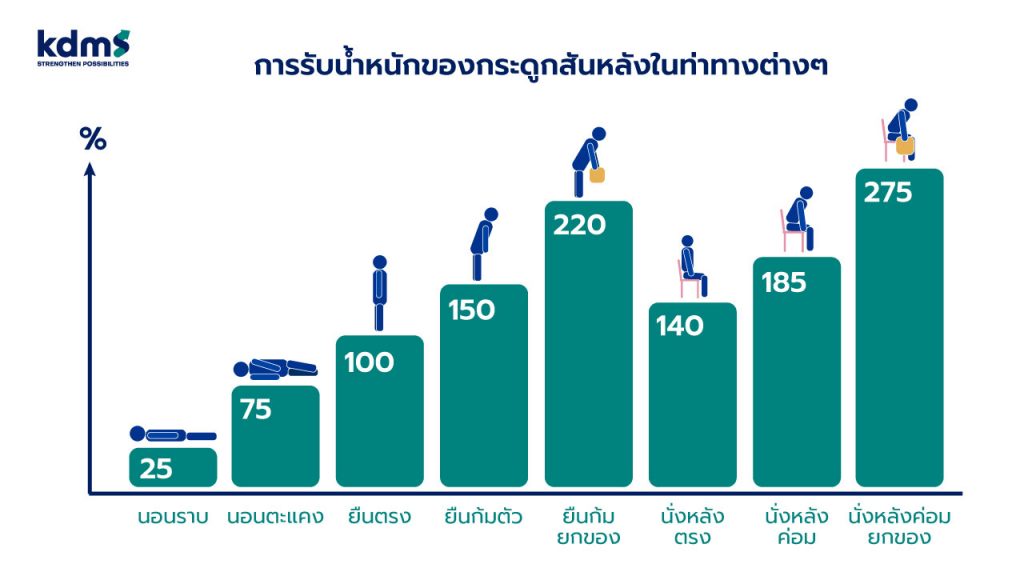
การรับน้ำหนักของกระดูกสันหลังในท่าทางต่างๆ
นอนราบ รับน้ำหนัก 25%
นอนตะแคง รับน้ำหนัก 75%
ยืนตรง รับน้ำหนัก 100%
ยืนก้มตัว รับน้ำหนัก 150%
ยืนก้มตัวและยกของ รับน้ำหนัก 220%
นั่งหลังตรง รับน้ำหนัก 140%
นั่งหลังค่อม รับน้ำหนัก 185%
นั่งหลังค่อมและยกของ รับน้ำหนัก 275%
จากรูปจะเห็นได้ว่าในท่ายืนหลังตรงปกติ กระดูกสันหลังของเราจะรับน้ำหนักเต็มๆ ที่ 100% อยู่แล้ว แต่หากอยู่ในท่านั่ง กระดูกสันหลังจะรับน้ำหนักมากขึ้นไปอีกที่ 140% นั่นเป็นเพราะน้ำหนักทั้งตัวไม่ได้ถูกแบ่งเบาไปที่ร่างกายท่อนล่าง แต่มากองรวมกันอยู่ที่ช่วงเอว ยิ่งถ้านั่งนานหลายชั่วโมงโดยไม่ลุกเดินบ้าง ก็ไม่ต่างจากการถือของหนักๆ โดยที่ไม่วางลงเลย จนทำให้เรารู้สึกปวดหลัง ซึ่งกลายเป็นปัญหาใหญ่ที่มนุษย์ออฟฟิศหลายคนต้องเจอนั่นเอง
อ่านบทความเพิ่มเติม: ออฟฟิศซินโดรม หายได้ด้วยศาสตร์ผสมผสานการรักษา
Q: จริงหรือไม่ที่การก้มหน้าเล่นโทรศัพท์มือถือนานๆ สามารถส่งผลต่อเนื่องกับกระดูกสันหลังได้ในระยะยาว
จริงๆ แล้วช่วงคอก็ถือเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของกระดูกสันหลังเช่นกัน ซึ่งมีหน้าที่ในการรับน้ำหนักศีรษะและทำให้มีการเคลื่อนไหวของคอ หลายคนที่เคยสงสัยว่าทำไมลองปรับโต๊ะทำงานให้เหมาะสมแล้วก็ยังรู้สึกปวดเมื่อยอยู่ เรื่องนี้อาจเป็นจุดเล็กๆ ที่เผลอมองข้ามไป
อย่างเช่นอวัยวะที่ 33 ของคนยุคนี้อย่างโทรศัพท์มือถือที่อยู่ติดตัวเราตลอดทั้งวัน เคยลองสังเกตกันบ้างหรือเปล่าว่าคุณใช้มันในท่าทางแบบไหน

จากภาพนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าการจัดท่าให้คอก็มีความสำคัญเช่นกัน เพราะในขณะที่คอของเราตั้งตรงปกติก็ยังรับน้ำหนักอยู่ที่ 5 กิโลกรัมแล้ว และยิ่งถ้าเราก้มลงไปเท่าไหร่ กล้ามเนื้อด้านหลังก็จะต้องออกแรงเยอะเพื่อดึงไม่ให้หัวตกไปด้านหน้า ยิ่งหากเราก้มหน้านานเป็นชั่วโมง ก็เท่ากับกล้ามเนื้อกำลังออกแรงอยู่เป็นชั่วโมงเช่นเดียวกัน และนั่นคือปัญหาที่ทำให้หลายคนรู้สึกปวดบริเวณคอ บ่า ไหล่
คำแนะนำง่ายๆ สำหรับคนที่อยากแก้ปัญหาการก้มคอโดยไม่รู้ตัว ให้นำหมอนใหญ่ๆ มาวางไว้บนตัก แล้ววางมือที่เราจับโทรศัพท์มือถือลงบนหมอนอีกทีหนึ่ง พยายามให้อยู่ในระดับสายตา ไม่ต้องก้ม ลองฝึกให้เคยชินจนเป็นนิสัย ถ้าหากทำได้ อาการปวดคอจะหายไปแน่นอน
Q: ปวดหลังแล้วไปหาหมอจัดกระดูก สามารถช่วยให้ดีขึ้นได้จริงไหม หรือเป็นการรักษาที่ปลายเหตุ
โดยส่วนใหญ่สาเหตุของการจัดกระดูกจะทำเพื่อรักษาผู้ที่มีภาวะกระดูกสันหลังคดหรือเอียง เพื่อที่จะจัดกระดูกให้ตรงขึ้น แต่ก่อนอื่นต้องแยกปัญหาก่อนว่าภาวะกระดูกสันหลังคดของเรามันเกิดจากอะไร
แบบแรกคือกระดูกสันหลังคดที่เกิดจากการที่กล้ามเนื้อปวด เมื่อย ตึง หรือบาดเจ็บ โดยปกติกล้ามเนื้อจะมีสองฝั่งทั้งซ้ายและขวา หากเกิดการตึงตัวหรือบาดเจ็บของแต่ละฝั่งที่ไม่เท่ากัน โดยธรรมชาติของร่างกายจะพยายามใช้กล้ามเนื้ออีกฝั่งมากขึ้น ทำให้เกิดลักษณะของกระดูกคดเนื่องจากอาการปวด ซึ่งหากเป็นเช่นนี้ การจัดกระดูกจะเป็นการช่วยผ่อนคลายกล้ามเนื้อบริเวณรอบๆ กระดูกสันหลังเพื่อให้มีความผ่อนคลายมากขึ้น และเมื่อการบาดเจ็บหรือตึงตัวของกล้ามเนื้อหลังเริ่มดีขึ้นแล้ว ร่างกายก็จะสามารถปรับสภาพให้กระดูกสันหลังกลับมาตรงได้เป็นปกติ
แต่ยังมีภาวะกระดูกสันหลังคดอีกแบบหนึ่งที่ยังไม่มีผลการศึกษาออกมาชัดเจนว่าการจัดกระดูกสามารถช่วยได้ นั่นคือภาวะกระดูกสันหลังคดที่เกิดจากความผิดปกติเชิงโครงสร้างของตัวกระดูกสันหลัง ที่พบได้บ่อยคือกลุ่มกระดูกสันหลังคดในวัยรุ่นที่ไม่ทราบสาเหตุ ซึ่งจะเกิดขึ้นกับเด็กในช่วงอายุประมาณ 10 ขวบขึ้นไป โดยอยู่ๆ กระดูกสันหลังมีการบิดหมุนและคดเอียงขึ้นมาเอง แต่ไม่ได้รู้สึกเจ็บปวดอะไร ซึ่งในทางการแพทย์จะพิจารณารักษาตามความรุนแรงของการคดเอียง หากเป็นมากแพทย์อาจจะแนะนำให้ใส่เสื้อเกราะดัดเพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้กระดูกสันหลังคดเอียงมากขึ้น
Q: การผ่าตัดหลังน่ากลัวสำหรับคนแก่จริงหรือเปล่า หากผ่าตัดแล้วต้องพักฟื้นนานแค่ไหน
คนส่วนใหญ่ที่มาผ่าตัดกระดูกสันหลังมักจะมีความกังวลอยู่ 2 อย่าง หนึ่งคือการเข้าใจว่าผ่าไปแล้วเดี๋ยวจะเป็นอัมพฤกษ์-อัมพาต เดินไม่ได้ และสองคือกลัวว่าถ้าผ่ากระดูกสันหลังแล้วจะต้องนอนติดเตียงหลายเดือน จึงจะลุกขึ้นมายืนหรือเดินได้ปกติอีกครั้ง
สำหรับความคิดที่ว่าผ่าตัดกระดูกสันหลังแล้วอาจจะเป็นอัมพฤกษ์-อัมพาตหรือไม่นั้น ต้องบอกว่าสองอย่างนี้ไม่ได้เกี่ยวข้องกันโดยตรง เพราะการผ่าตัดเป็นไปเพื่อแก้ไขการกดทับของเส้นประสาท ทำให้หลังจากผ่าตัดไปแล้ว อาการชาหรือปวดร้าวลงขาจะค่อยๆ ดีขึ้นทันทีจนสามารถยืนและเดินได้ดีขึ้น หากจะถามถึงความเสี่ยงก็ต้องบอกว่ามีน้อยมากๆ แต่โอกาสที่ร่างกายจะดีขึ้นจากการผ่าตัดนั้นมีมากกว่าความเสี่ยงที่จะได้รับอย่างแน่นอน
การผ่าตัดกระดูกสันหลังในปัจจุบันจะมีอยู่ 2 แบบ คือแบบเปิดแผลปกติ ซึ่งใช้เวลาพักฟื้นเพียง 5-7 วันก็สามารถลุกเดินและกลับบ้านได้แล้ว ส่วนอีกแบบหนึ่งจะเป็นการผ่าตัดรักษาแบบแผลเล็ก (Minimally Invasive Surgery) ซึ่งจะมีทั้งแบบส่องกล้อง และการเจาะรูเชื่อมกระดูกทางด้านข้าง ข้อดีคือแผลเล็ก บาดเจ็บน้อย เสียเลือดน้อย และผู้ป่วยก็ใช้เวลาพักฟื้นน้อยกว่าเพียงแค่ 3-4 วันเท่านั้น


 history
history  appointment
appointment 





 451,000* บาท
451,000* บาท
 สิ้นสุด 30/06/2024
สิ้นสุด 30/06/2024